介绍:
得了胆总管结石怎么办?
How to deal with Common Bile Duct Stones?
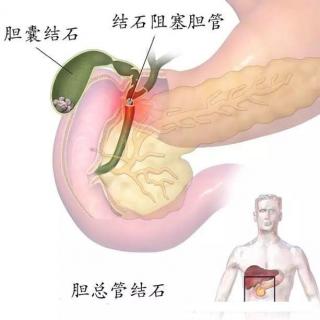
胆总管结石从何而来?
Where is Common Bile Duct Stones (CBDS) from?
The common bile duct (CBD) comes from the confluence of common hepatic duct and cystic duct and opens at the great duodenal papilla after meeting with the main pancreatic duct. It is a long tube which leads the bile synthesized in the liver to the intestine to digest the food.
Common Bile duct stones (CBDS) are classified into primary stones arising in the bile duct andsecondary stones from the gallbladder. The former is brown pigment stones while most of the latter is black pigment or cholesterol ones.
Currently, the incidence of CBD stones in China which rises with the age is 0.5% -3%, and increases gradually.
胆总管是由肝总管和胆囊管汇合形成,与主胰管汇合开口于十二指肠rutou,其主要作用是使由肝脏产生的胆汁排入十二指肠,发挥消化作用。胆总管结石分为原发性结石和继发性结石。原发性结石是指在胆总管中自发形成的结石,多为棕色胆色素类结石。继发性结石是指从胆囊排入胆总管的结石,大多为胆固醇结石或黑色胆色素结石。目前我国胆管结石的发病率为0.5%-3%,并呈上升趋势,同时随着年龄的增长而增加。
得了胆总管结石会有哪些不适?
What is the probable feeling if you have CBDS ?
The patients with CBDS often have paroxysmal colic or swelling pain in the upper-right region of the abdomen after the greasy food which can be radiated to right back and shoulder.The pain can last from 30 minutes to smatcheveral hours. The Patient may have nausea, vomiting, chilling andhigh fever beyond 39℃ whose urine is like dark tea. One or two days later his skin and the white part of the eyes will turn into yellow gradually. Talking nonsense, unconsciousness and coma means severe cases and life-threatening status.
有了胆总管结石的患者,常会在进食油腻食物后发生右上腹阵发性胀痛或绞痛,也可呈持续性疼痛阵发性加剧,可向右肩背部放射,疼痛可持续30分钟至数个小时不等;严重时可以有恶心呕吐,发冷发抖然后高热可达39℃以上,小便颜色加深如茶色,进而出现眼白和皮肤发黄。最严重的会引起胡言乱语、神志不清和昏迷等。
得了胆总管结石怎么办?
How to do with CBDS?
CBDS must be removed as early as possible once they are found. There are two minimally invasive techniques as described below.
ERCP is an effective treatment for CBDS. The stones are pulled out of common bile duct through the scope which is inserted from mouth to duodenum. The success rate is about 90%. The technique is associated with shorter operation time, shorter hospital stay and quicker recovery compared to the traditional surgery,
Laparoscopic surgery is performed via four small abdominal incision. It allows for single-stage treatment of CBDS with removal of the gallbladder as part of the same procedure. The success rate is nearly 100%. Laparoscopic surgery has the advantage of reserve of the sphincter of Oddi function. And it can be performed without T-tube insertion by which the whole treatment duration decreases from about 2 months to 1 week.
发现胆总管结石无论有无不适,都应尽早取出结石,目前临床上常见的微创取石方式有两种:
逆行胆胰管造影术(ERCP):ERCP形式上和做胃镜一样,通过插一根内镜至十二指肠将胆管中的结石从胆管内取出,置入肠腔内排出体外,总体成功率约90%。ERCP取石不需要开刀,局部麻醉下就可进行,创伤小,手术时间短、手术后观察两天即可出院。
腹腔镜微创手术,即在肚子上打4个小洞进行的微创手术,一般要求胆总管扩张8mm以上,成功率基本达到100%。一次手术可解决胆囊和胆总管两处问题,大多数患者术后一周即可出院、恢复快。同时不影响rutou括约肌功能。即使是有过胆道手术史或其他上腹部手术史的患者基本也能通过腹腔镜微创手术成功。
1. common bile duct胆总管;common hepatic duct 肝总管; cystic duct 胆囊管
2. bile [baɪl] n.胆汁; 愤怒; 坏脾气;
3. confluence [ˈkɒnfluəns] n.(河流的)汇合处; 汇流处; (事物的)汇合; 汇流
the confluence of A and B :a 和 b 的汇合处
4. papilla [pə'pɪlə] n.rutou; 小rutou状突起; 丘疹; 小脓包
5. synthesize [ˈsɪnθəsaɪz] vt.综合; 人工合成; vi.合成; 综合;
6. pigment stones 胆色素结石
pigment [ˈpɪgmənt] n.颜料,色料; [生]色素;vt.给…着色;vi.呈现颜色;
7. paroxysmal[ˌpærək'sɪzməl] adj.发作性的,爆发性的; 阵发性;
8. colic[ˈkɒlɪk] n.绞痛,疝痛,疝气
9. greasy[ˈgri:si] adj.油腻的; 谄媚的; 含脂肪多的;
10. 内镜逆行性胰胆管造影术(Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography, ERCP)
资料来源:仁济医院国际医疗RenjiHospital
Bgm-anything but ordinary
撰稿讲解:福建医科大学 淑铉铉铉
大家还在听